Shark Brains vs. Dolphin Brains – Exploring the Minds of the Deep
Sharks and dolphins are like the rock stars of the ocean, each possessing unique qualities that have intrigued scientists and marine enthusiasts for generations.
These underwater wonders boast impressive brains, but how do their gray matter stacks up against each other in the grand arena of oceanic intellect?
Let’s dive deep into the world of shark and dolphin brains to uncover the secrets of these incredible marine creatures!
Shark Brains: The Stealthy Cerebral Powerhouses
When you think of sharks, you probably picture their sleek, predatory bodies slicing through the water with unmatched grace and ferocity. But beneath those intimidating exteriors lies a brain that’s been honed by millions of years of evolution.
Anatomy of a Shark Brain
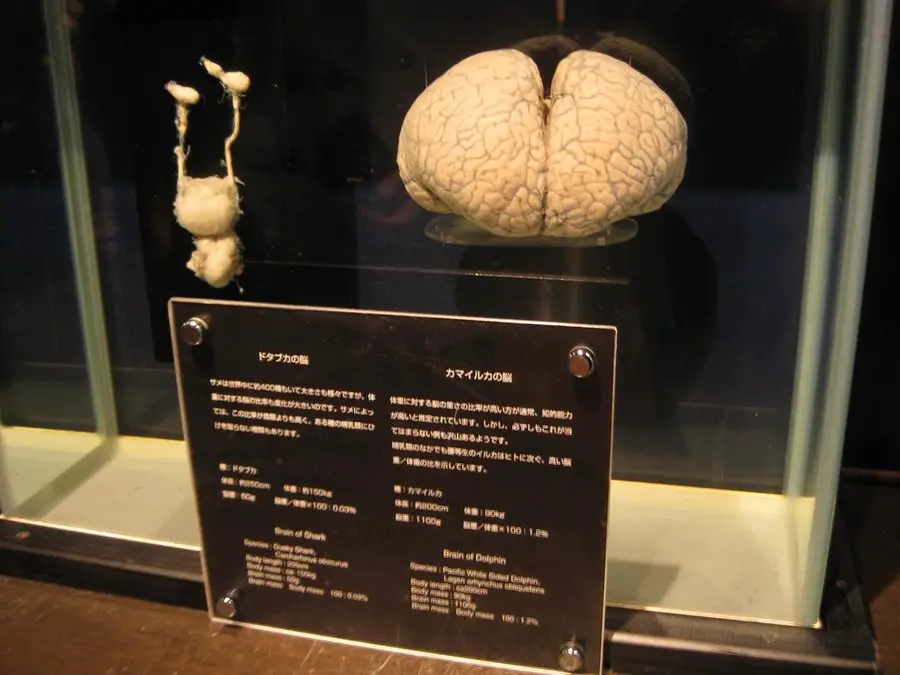
Shark brains are no slouch, even if they’re relatively small when compared to their body size.
These cerebral powerhouses account for approximately 0.2% of a shark’s total body weight, which might seem like a pittance compared to our own brains, which make up about 2% of our body weight. But don’t let the size fool you; shark brains are intricate and sophisticated.
A shark’s brain can be divided into three primary regions:
- The Forebrain: Responsible for higher-order functions like learning, memory, and problem-solving. Yep, even sharks do some critical thinking!
- The Midbrain: Coordinates movement and processes sensory information, crucial for their hunting prowess.
- The Hindbrain: Handles basic functions like breathing and heart rate, ensuring their survival.

Sensory Marvels
One of the most remarkable features of a shark’s brain is its sensory capabilities. Sharks are often hailed as the bloodhounds of the sea, thanks to their impeccable sense of smell.
Their olfactory bulbs, the brain structures responsible for processing smells, are surprisingly large. This incredible olfactory prowess helps sharks locate prey from miles away.
But that’s not all; sharks are no slouches in the hearing and vision departments either. Their eyes, strategically placed on the sides of their heads, provide them with an expansive field of view, allowing them to detect movement with precision.
Combine this with their incredible ability to sense electric fields, and you’ve got a predator that’s a force to be reckoned with!
Dolphin Brains: The Whimsical Wizards of the Sea
If sharks are the silent assassins of the ocean, dolphins are its playful geniuses. These enchanting creatures are known for their incredible intelligence and social prowess, and their brains reflect these remarkable qualities.
Anatomy of a Dolphin Brain
Dolphin brains are notably larger when compared to sharks, comprising around 1.5% of their total body weight, a feat unrivaled in the animal kingdom. These cerebral giants are the brainiacs of the deep, boasting several unique features that set them apart:
- A Large Neocortex: This part of the brain is responsible for higher-order functions like learning, memory, and problem-solving, making dolphins remarkably clever.
- A Large Hippocampus: The hippocampus is vital for memory and spatial navigation, allowing dolphins to remember complex information and navigate their vast oceanic world.
- A Large Corpus Callosum: This band of nerve fibers connects the two hemispheres of the brain, facilitating communication between different brain regions. In dolphins, this structure is especially well-developed, enabling rapid information processing.

The Enigma of Dolphin Intelligence
Dolphins’ large brains are believed to underpin their intelligence and complex social behaviors. Unlike sharks, dolphins are not just lone wolves prowling the seas; they are highly social creatures, often found in close-knit pods. Their intelligence shines in various ways:
- Learning Complex Tasks: Dolphins are known for their ability to learn and perform intricate tasks, showcasing problem-solving skills that rival some land-dwelling mammals.
- Long-Term Memory: These marine geniuses possess impressive long-term memory, allowing them to remember specific individuals and events over extended periods.
- Communication: Dolphins are not just masters of body language; they also use a wide range of vocalizations to communicate with each other. It’s almost like they have their own underwater language!
A Brainy Showdown: Shark vs. Dolphin
Now that we’ve explored the unique features of shark and dolphin brains, let’s break down the key differences in a handy table for easy comparison:
| Feature | Shark | Dolphin |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Small (0.2% of body weight) | Large (1.5% of body weight) |
| Complexity | Less complex | More complex |
| Neocortex | Small | Large |
| Hippocampus | Small | Large |
| Corpus Callosum | Small | Large |
Implications for Behavior
The differences in brain structure between sharks and dolphins lead to striking variations in their behaviors:
- Sharks: These solitary hunters may not be winning any Nobel Prizes, but their streamlined brains are perfectly tailored for their solitary, predatory lifestyle. They rely on instinct and sensory acuity to thrive in their environment.
- Dolphins: With their larger, more complex brains, dolphins exhibit highly developed problem-solving abilities and social behaviors. Their intelligence is a key factor in their ability to navigate complex social hierarchies and thrive in their tight-knit communities.
Conclusion
In the world of marine marvels, sharks and dolphins are the undisputed champions, each with their unique set of skills and attributes.
While shark brains are smaller and less complex, suited perfectly for their solitary hunting, dolphins boast larger, more intricate brains that power their intelligence and social interactions.
So, the next time you encounter these incredible creatures in the deep blue, you’ll have a deeper understanding of the fascinating minds that lie beneath the waves!
